Psychology
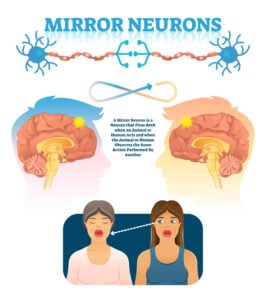
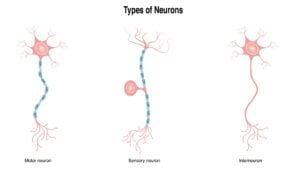
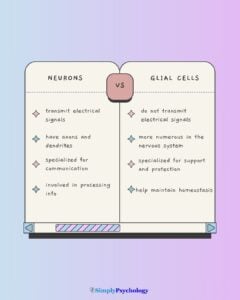
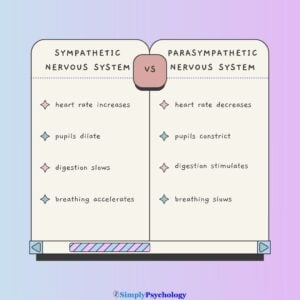
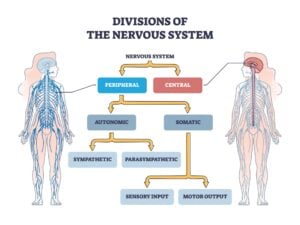
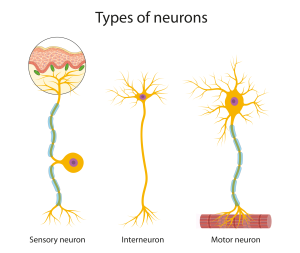
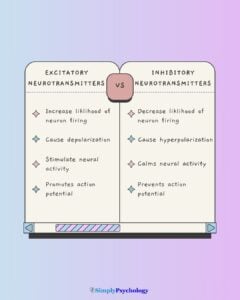
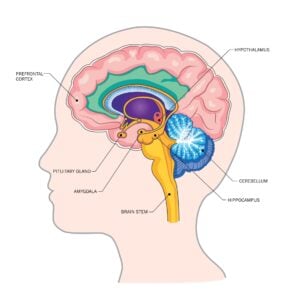
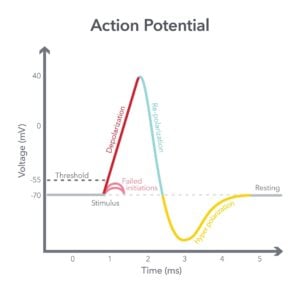
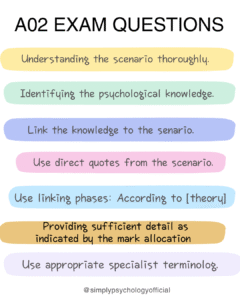
Explore a wide array of psychological theories and concepts that explain human thoughts, behaviors, and emotions. From foundational theories like behaviorism and psychoanalysis to contemporary approaches such as cognitive psychology and neuroscience.